Vinyl windows (also known as PVC Windows or uPVC Windows) are a popular choice for homeowners due to their low maintenance, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. They are resistant to moisture, corrosion, and rot, making them ideal for various climates. However, they may have limitations in large openings, extreme heat, or high-end aesthetic demands.
What Are Vinyl Windows? (Material & Structure Overview)
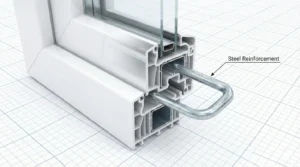
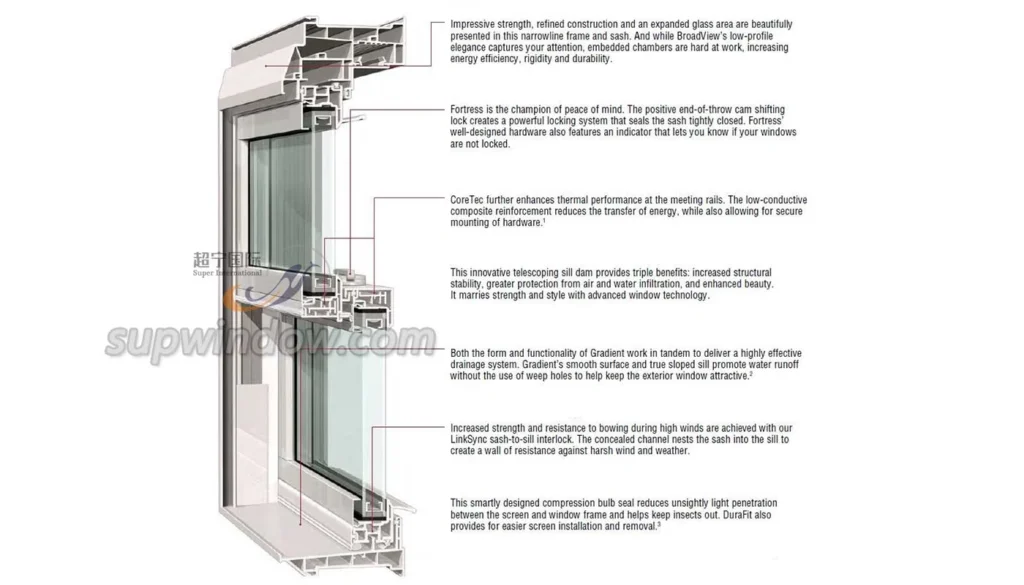
Vinyl Window Construction & Multi-Chamber Design
Vinyl windows are primarily made of uPVC (unplasticized polyvinyl chloride). High-quality frames feature multiple internal chambers that enhance insulation, reduce air infiltration, and increase rigidity. Corner welds provide structural integrity, preventing gaps and reducing maintenance issues.
PVC vs Vinyl Windows: Key Differences
PVC windows are the broader category, while uPVC refers to rigid, unplasticized variants with superior durability. Modern manufacturing ensures low expansion rates, improved UV resistance, and reinforced frame profiles suitable for residential and light commercial applications.
Common Vinyl Window Styles
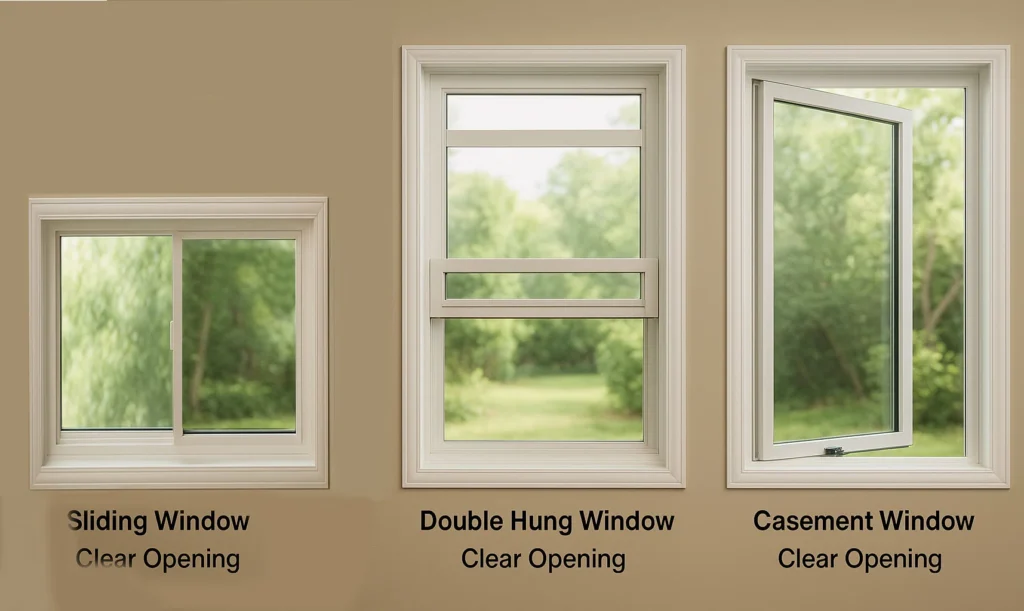
Popular styles include double-hung, sliding, casement, and impact-rated models. Each has distinct operational mechanics. For instance, double-hung windows allow top and bottom sash movement, while sliders move horizontally for wider openings.

Are Vinyl Windows a Good Choice for Your Home?
Situations Where Vinyl Windows Excel
PVC Windows excel in moderate to high-humidity regions due to moisture resistance. They are ideal for replacement projects requiring low maintenance and energy-efficient solutions. Their insulated frames and Low-E glass options help reduce heating and cooling costs.
Situations Where Vinyl May Not Be Ideal
Large picture windows or structural openings may challenge frame rigidity. In regions with extreme heat or high UV exposure, lower-quality uPVC can warp or fade. High-end custom aesthetics may favor wood or composite alternatives.

Vinyl Windows Pros and Cons
Pros
Energy Efficiency: Multi-chamber frames and double/triple-pane glass reduce heat transfer.
Cost-Effective: Lower initial cost compared to wood or fiberglass.
Low Maintenance: No painting or sealing needed.
Moisture & Rot Resistant: Ideal for coastal and humid regions.
Variety of Colors & Finishes: Dark, neutral, and laminated finishes available.
Cons
Thermal Expansion: Large units may expand or contract with temperature changes.
Color Fading: Prolonged UV exposure can lighten darker finishes.
Structural Limitations: Not ideal for oversized openings without reinforcement.
Limited Paintability: Difficult to repaint without specialized coatings.
Vinyl Windows Performance Explained
Energy Efficiency Comparison
| Material | U-Factor | SHGC | VT | Maintenance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Window | 0.25–0.30 | 0.25–0.35 | 0.45–0.55 | Low | $150–$400/frame |
| Wood | 0.30–0.35 | 0.25–0.35 | 0.45–0.55 | Medium | $300–$800/frame |
| Aluminum | 0.35–0.45 | 0.25–0.35 | 0.50–0.60 | Low | $200–$500/frame |
| Fiberglass | 0.25–0.30 | 0.25–0.35 | 0.45–0.55 | Low | $400–$700/frame |
Energy-efficient PVC Windows often include argon or krypton gas-filled IGUs and Low-E coatings, reflecting heat in summer and retaining it in winter.
Lifespan & Durability
High-quality uPVC Windows can last 20–40 years. Durability depends on material grade, climate exposure, installation quality, and maintenance frequency.
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Tools & Materials List:
Soft microfiber cloth: Cleaning without scratching
Mild detergent / Isopropyl alcohol: Dirt and grime removal
Silicone or PTFE lubricant: Smooth sash movement
Small brush / vacuum nozzle: Dust removal in tracks
Level & tape measure: Inspect alignment
Replacement weatherstripping: Seal drafty areas
Step-by-Step Maintenance:
Remove dust from frames and tracks using a brush or vacuum.
Clean glass and frames with mild detergent and soft cloth.
Lubricate moving parts with silicone spray; avoid oil-based lubricants.
Inspect seals and weatherstripping; replace if brittle or damaged.
Check sash alignment with a level; adjust or shim if necessary.
Troubleshooting Common Issues:
Condensation: Check seal integrity, consider IGU upgrade.
Sticky sashes: Lubricate tracks; ensure no debris.
Warping / misalignment: Evaluate for thermal expansion; minor adjustments may suffice.
Seal failure: Replace gasket or consider professional reglazing.
Vinyl Windows vs Other Materials
| Feature | PVC Windows | Wood | Aluminum | Fiberglass | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | 20–40 yrs | 15–30 yrs | 25–35 yrs | 30–50 yrs | |
| Maintenance | Low | Medium | Low | Low | |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Medium | Medium-Low | High | |
| Cost | Low-Medium | Medium-High | Medium | Medium-High | |
| Structural Strength | Medium | High | High | High | |
| Aesthetic Options | Multiple | Customizable | Limited | Limited |
PVC Windows are cost-effective and energy-efficient, while wood offers premium aesthetics. Fiberglass is strong and stable, suitable for large openings, and aluminum is durable but less insulating.

Types of Vinyl Windows & Best Use Cases
Double-Hung PVC Windows
Best for traditional homes; allow ventilation top and bottom.
Sliding( Slider)Windows
Ideal for wide openings and rooms needing unobstructed views.
Impact-Rated PVC Windows
Hurricane or storm zones; reinforced frames and laminated glass.
Basement, Mobile Home, & Screen Porch Applications
Smaller units, moisture-resistant, often include ventilation or tilt-out features.

Cost & Time Estimates
Replacement Costs
Standard 36″x48″ PVC Window: $150–$400
Upgraded Low-E argon double-pane: $250–$450
Installation Time
Full-frame replacement: 2–3 hours per window
Pocket replacement: 1–2 hours per window
Hidden Costs:
Labor, disposal of old windows, frame modifications, trim work
Installation Guidelines & Mistakes to Avoid
Full-Frame vs Pocket Replacement
Full-frame: Removes entire old window; better for energy efficiency.
Pocket replacement: Fits into existing frame; faster, less intrusive.
Common Mistakes
Failing to level window before securing
Gaps in sealant causing drafts
Using inappropriate fasteners or screws
Ignoring thermal expansion allowances
Expert Tips
Measure multiple points to ensure correct fit
Use professional-grade sealant and flashing
Avoid low-quality recycled PVC in hot climates
Check DP ratings for wind resistance
When to Repair vs When to Replace
Minor sash sticking or condensation: repair
Warping, repeated seal failure, or structural weakness: replace
Evaluate cost-benefit: replacement often improves efficiency and resale value
Expert Tips
Choose 100% virgin uPVC for longevity
Match window type to climate (impact-rated for coastal areas)
Install Low-E glass with argon/krypton fill for energy efficiency
Avoid shortcuts during installation; improper alignment reduces lifespan
Regular inspection ensures thermal and structural performance

FAQ Section
-
1. Are vinyl windows bad?
No, high-quality PVC Windows are durable, energy-efficient, and low maintenance.
-
2. How long do vinyl windows last?
20–40 years depending on material quality and installation.
-
3. Are vinyl windows good in hot climates?
uPVC Windows perform well with reinforced frames and reflective coatings.
-
4. Can vinyl windows be black or dark brown?
Yes, modern finishes allow dark colors with UV-resistant coatings.
-
5. How often do vinyl windows need to be replaced?
Typically every 20–40 years or if structural/insulation issues arise.
-
6. Are vinyl windows better than wood?
Cost-effective, low maintenance, energy-efficient; wood offers higher aesthetics.
-
7. What are common problems with vinyl windows?
Warping, sash sticking, condensation, seal failure.
-
8. Are vinyl windows fire-rated?
PVC is self-extinguishing; consult local building codes for rating.
-
9. Are vinyl windows impact-resistant?
Impact-rated models are available for hurricane zones.
-
10. How much do replacement PVC Windows cost?
$150–$450 per unit depending on size and upgrades.